前言
之前在印象笔记中写过一个python+opencv版的最大连通域标记的程序,当时使用的是opencv2版本中的findContours函数作为载体,由于没有在意findContours中的各个contours之间的hierarchy关系,后来在一次实验中发现这种方式是有不足之处的,最方便的还是使用连通域标记算法将图像标记为各个连通域,然后在取连通域最大的区域这种方法。
错误的版本
先贴出错误的版本,这个版本的想法是使用findContours函数找到各个连通域的contours,然后选取contours面积最大的那个作为目标区域,并将其填充。findContours使用的是EXTERNAL的方式标记边缘。显然这种方法如果是一个大的连通域里面是中空的,则标记后的最大连通域会将中间空的部分填充上,因此出错。
Python版
之前的python版主要实现功能是利用opencv获取最大连通区域并去除。将之前在印象笔记里写的记录摘抄下来如下:
主要使用了如下方法:
- 首先通过findContours函数找到二值图像中的所有边界(这块看需要调节里面的参数)
- 然后通过contourArea函数计算每个边界内的面积
- 最后通过fillConvexPoly函数将面积最大的边界内部涂成背景
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.imread('bw.bmp')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#find contours of all the components and holes
gray_temp = gray.copy() #copy the gray image because function
#findContours will change the imput image into another
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(gray_temp, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
#show the contours of the imput image
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 255), 2)
plt.figure('original image with contours'), plt.imshow(img, cmap = 'gray')
#find the max area of all the contours and fill it with 0
area = []
for i in xrange(len(contours)):
area.append(cv2.contourArea(contours[i]))
max_idx = np.argmax(area)
cv2.fillConvexPoly(gray, contours[max_idx], 0)
#show image without max connect components
plt.figure('remove max connect com'), plt.imshow(gray, cmap = 'gray')
plt.show()
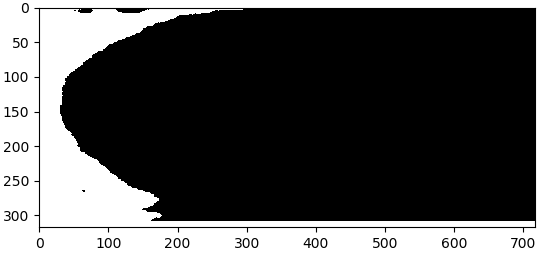
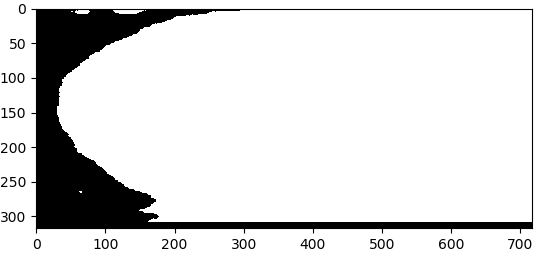
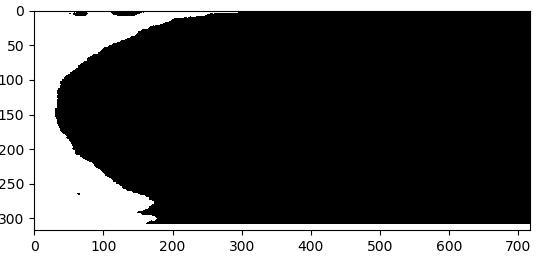
结果如下:


分析上述结果可以发现存在两个问题:
- 使用findContours函数检测边缘时如果最大连通域出现中空情况,则结果会将中空的部分填充上,得到错误的结果,本图因为中间没空,所以看起来效果是对的。
- 使用fillConvexPoly这个函数是有缺陷的,如果最大连通域不是凸的,则会得到错误的填充结果。
c++版
void findLargesrArea(Mat srcImage, Mat &dstImage)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(srcImage.clone(), contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
double max_area = 0;
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
if(contourArea(contours[i]) > max_area)
{
max_area = contourArea(contours[i]);
index = i;
}
}
//cout << "max_index: " << index << endl;
dstImage = Mat::zeros(srcImage.rows, srcImage.cols, srcImage.type());
drawContours(dstImage, contours, index, Scalar(255));
imfill(dstImage, dstImage);
}
void imfill(Mat srcimage, Mat &dstimage)
{
Size m_Size = srcimage.size();
Mat temimage = Mat::zeros(m_Size.height + 2, m_Size.width + 2, srcimage.type());
srcimage.copyTo(temimage(Range(1, m_Size.height + 1), Range(1, m_Size.width + 1)));
floodFill(temimage, Point(0,0), Scalar(255));
Mat cutImg;
temimage(Range(1, m_Size.height + 1), Range(1, m_Size.width + 1)).copyTo(cutImg);
dstimage = srcimage | (~cutImg);
}
c++这个版本存在上述第1个问题,但是不存在第2个问题,原因是其使用了自定义的imfill函数,避免了图像非凸出现错误的情况。
改进的版本
Python版
最近发现图像处理库skimage很好用,因此用skimage写了一个函数用于标记最大连通域:
def largestConnectComponent(bw_img, ):
'''
compute largest Connect component of an labeled image
Parameters:
---
bw_img:
binary image
Example:
---
>>> lcc = largestConnectComponent(bw_img)
'''
labeled_img, num = label(bw_img, neighbors=4, background=0, return_num=True)
# plt.figure(), plt.imshow(labeled_img, 'gray')
# max_label = 0
max_label = 1
max_num = 0
for i in range(1, num+1): # 这里从1开始,防止将背景设置为最大连通域
if np.sum(labeled_img == i) > max_num:
max_num = np.sum(labeled_img == i)
max_label = i
lcc = (labeled_img == max_label)
return lcc
注意(2018.10.10添加)
有一次我在使用的时候发现有个参数还挺重要,就是这个max_label,如果把它设置为0,那么当一张图像只有一个连通域的时候,其结果正好是原始图像的反。
检查代码发现在这个地方:lcc = (labeled_img == max_label).如果只有一个最大连通域,那么函数不会执行for循环,直接进入lcc = (labeled_img == max_label),此时如果max_label如果是0,则会直接把背景当做最大连通域了,因此必须把max_label设置为1.
c++版
由于opencv3中增加了连通域标记函数,因此使得查找最大连通域变得更加容易。代码如下:
void DefectsDetector::LargestConnecttedComponent(Mat srcImage, Mat &dstImage)
{
Mat temp;
Mat labels;
srcImage.copyTo(temp);
//1. 标记连通域
int n_comps = connectedComponents(temp, labels, 4, CV_16U);
vector<int> histogram_of_labels;
for (int i = 0; i < n_comps; i++)//初始化labels的个数为0
{
histogram_of_labels.push_back(0);
}
int rows = labels.rows;
int cols = labels.cols;
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) //计算每个labels的个数
{
for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++)
{
histogram_of_labels.at(labels.at<unsigned short>(row, col)) += 1;
}
}
histogram_of_labels.at(0) = 0; //将背景的labels个数设置为0
//2. 计算最大的连通域labels索引
int maximum = 0;
int max_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n_comps; i++)
{
if (histogram_of_labels.at(i) > maximum)
{
maximum = histogram_of_labels.at(i);
max_idx = i;
}
}
//3. 将最大连通域标记为1
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++)
{
if (labels.at<unsigned short>(row, col) == max_idx)
{
labels.at<unsigned short>(row, col) = 255;
}
else
{
labels.at<unsigned short>(row, col) = 0;
}
}
}
//4. 将图像更改为CV_8U格式
labels.convertTo(dstImage, CV_8U);
}